If you’re lying awake at 2 AM with your mind racing through tomorrow’s to-do list, you’re in good company. According to the National Sleep Foundation, 63 percent of Americans say their sleep needs aren’t being met during the week. For busy professionals, poor sleep doesn’t stay in the bedroom—it follows you into morning meetings, afternoon energy crashes, and those moments when patience runs thin at home.
When I’m running on empty, it shows up everywhere. I’m reaching for that third cup of coffee, struggling to focus during important calls, and feeling like I’m just surviving instead of thriving.
Before you consider prescription sleep aids, try looking at what’s on your plate. Certain foods are naturally rich in sleep-supporting nutrients that can help you fall asleep faster, stay asleep longer, and wake up genuinely refreshed.
Here are nine research-backed foods and drinks that may transform your nights—and your days.
The Sleep-Supporting Powerhouses
1. Walnuts
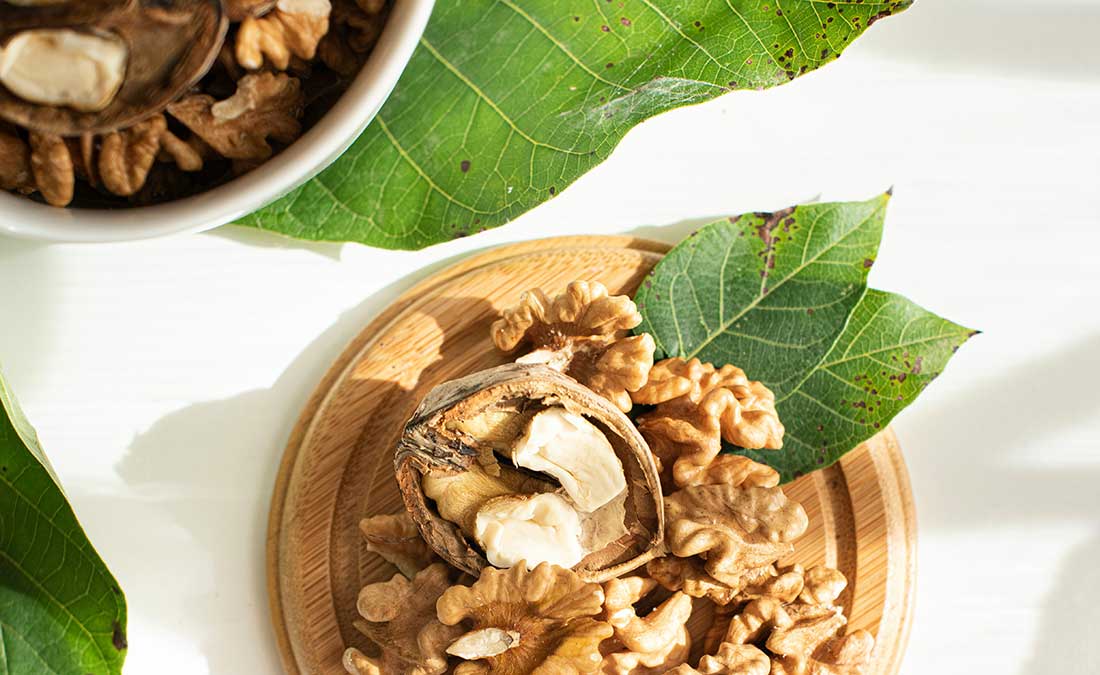

A handful of walnuts (about 1/3 cup or 14 halves) might be your ticket to better sleep. A recent randomized controlled trial published in Food & Function found that eating walnuts daily boosted levels of melatonin—the hormone that regulates sleep. People in the study fell asleep more quickly and reported significantly better sleep quality.
Walnuts deliver a unique combination of melatonin, magnesium, tryptophan, and B vitamins. Sprinkle them on oatmeal or roasted vegetables, stir into yogurt, or blend into smoothies. The easiest fix? Keep a bag in your desk drawer for an evening snack.
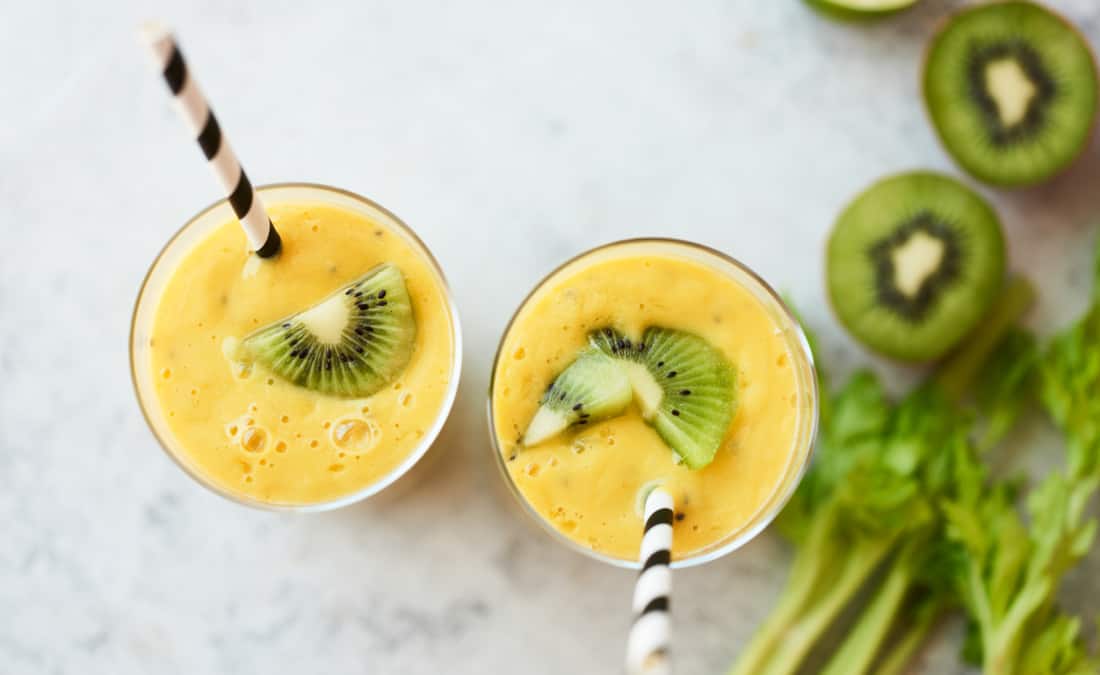
2. Kiwi
This fuzzy fruit packs a serious sleep punch. Eating 1-2 kiwis before bed has been linked to falling asleep 35% faster, staying asleep longer, and waking up less during the night. The magic lies in kiwi’s naturally occurring serotonin, vitamin C, and carotenoids, which promote sleep and reduce inflammation.
Slice one up after dinner—it’s refreshing, naturally sweet, and can easily replace that evening dessert craving. Get both a sleep-inducing and gut-healthy boost (thanks kefir!) with one of these Mango Kiwi Kefir Lime Smoothies.
3. Fatty Fish
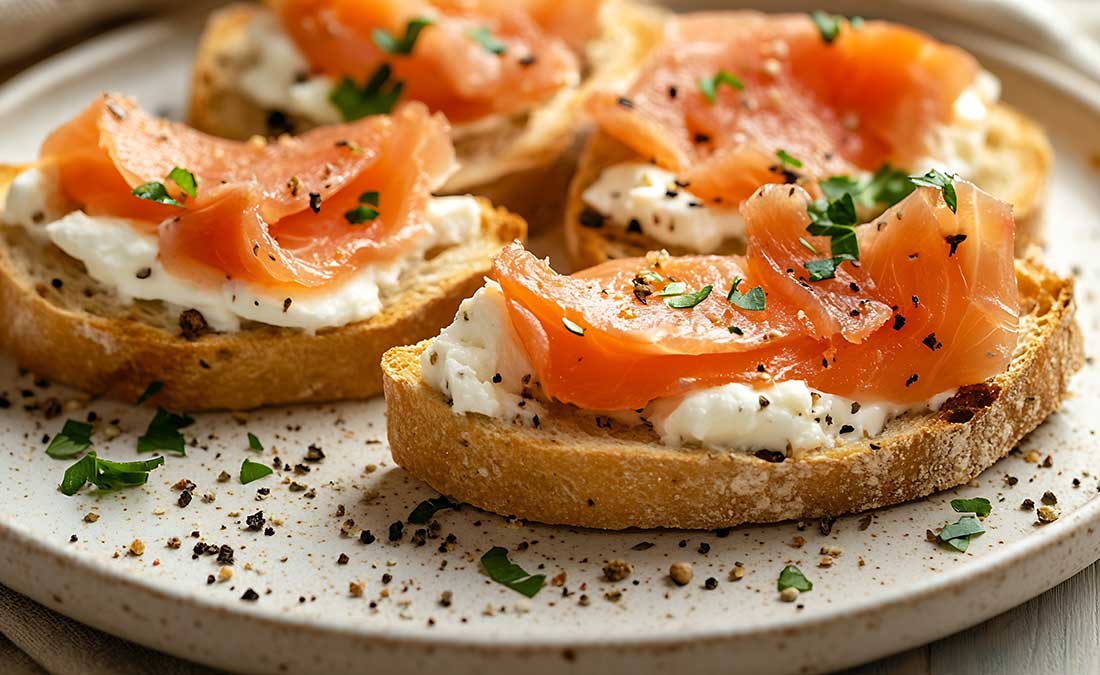

Salmon, tuna, and mackerel provide a triple threat of sleep-supporting nutrients: omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, and tryptophan. These work together to boost serotonin production, which your body needs to make melatonin. Research in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition shows that tryptophan-rich foods improve morning alertness by enhancing overnight rest quality.
Short on time? Keep sustainably-caught canned or smoked salmon on hand. Enjoy it on crackers with plain Greek yogurt and fresh dill for a quick, sleep-friendly dinner.
The Comfort Food Sleep Helpers
4. Oats
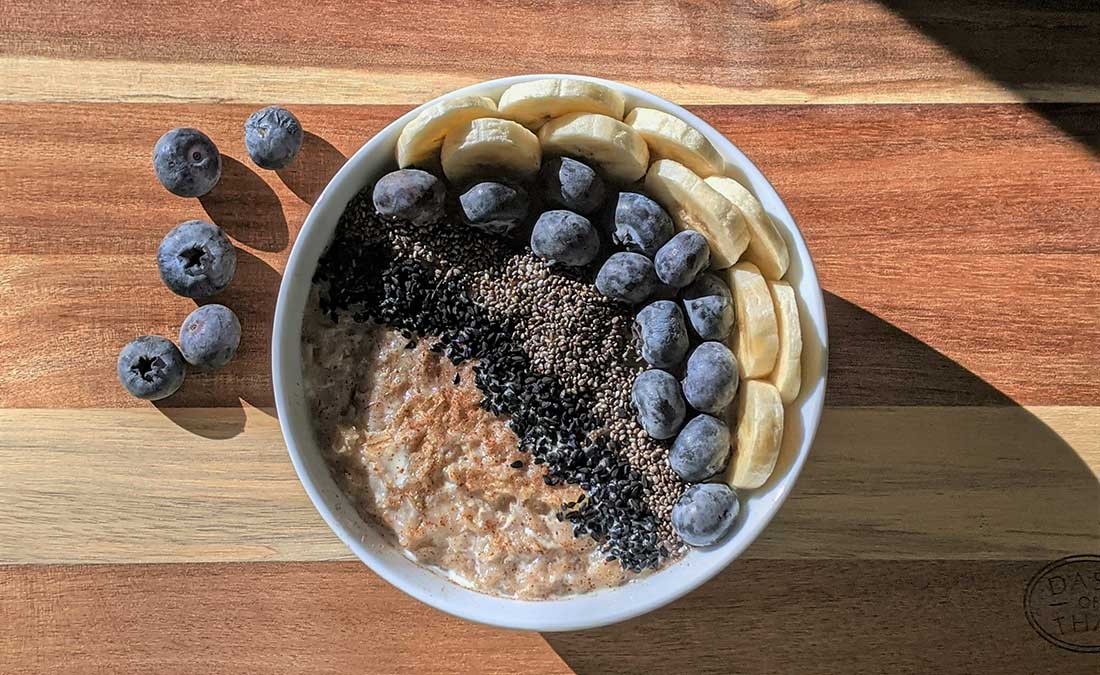

That bowl of oatmeal might do more than fill you up—it could help you sleep through the night. Oats, along with rice and barley, provide both melatonin and tryptophan. As complex carbohydrates, they trigger insulin release, helping tryptophan reach your brain where it converts to serotonin and then melatonin. The result? Natural relaxation and better sleep support.
5. Dairy
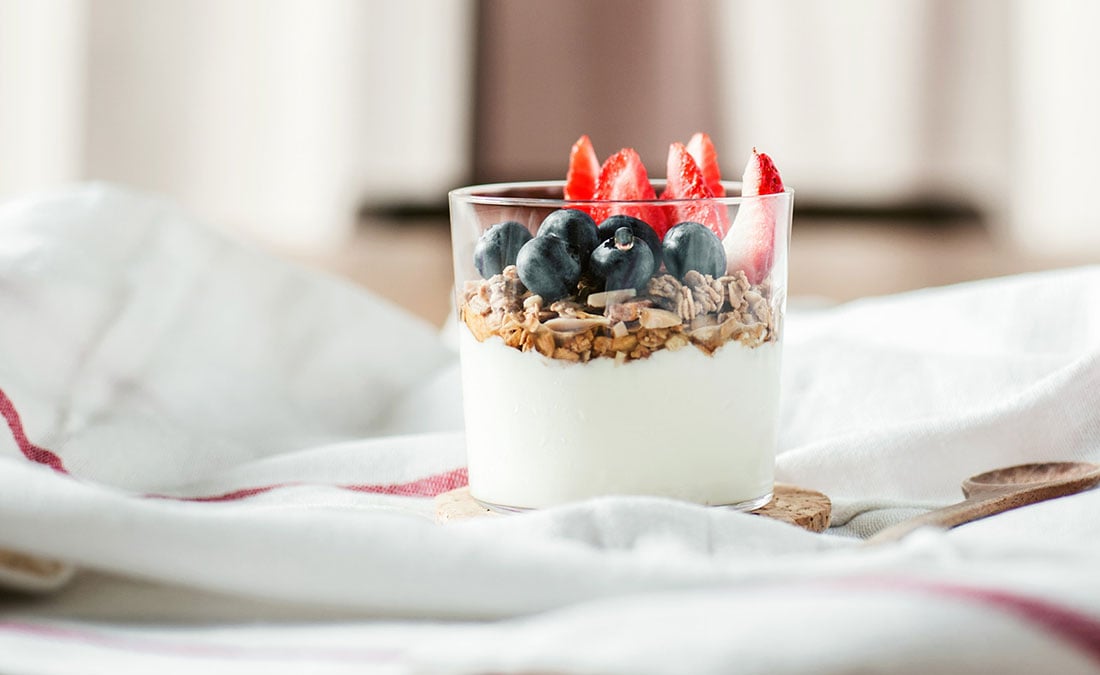

There’s real science behind that old “warm milk before bed” advice. Dairy foods like milk, yogurt, and cheese are rich in calcium, which helps your body use tryptophan to produce melatonin. Research suggests there may even be a direct correlation between calcium intake and sleep quality.
No time to cook? A small bowl of Greek yogurt topped with fruit makes a protein-rich evening snack that works double duty.
6. Bananas
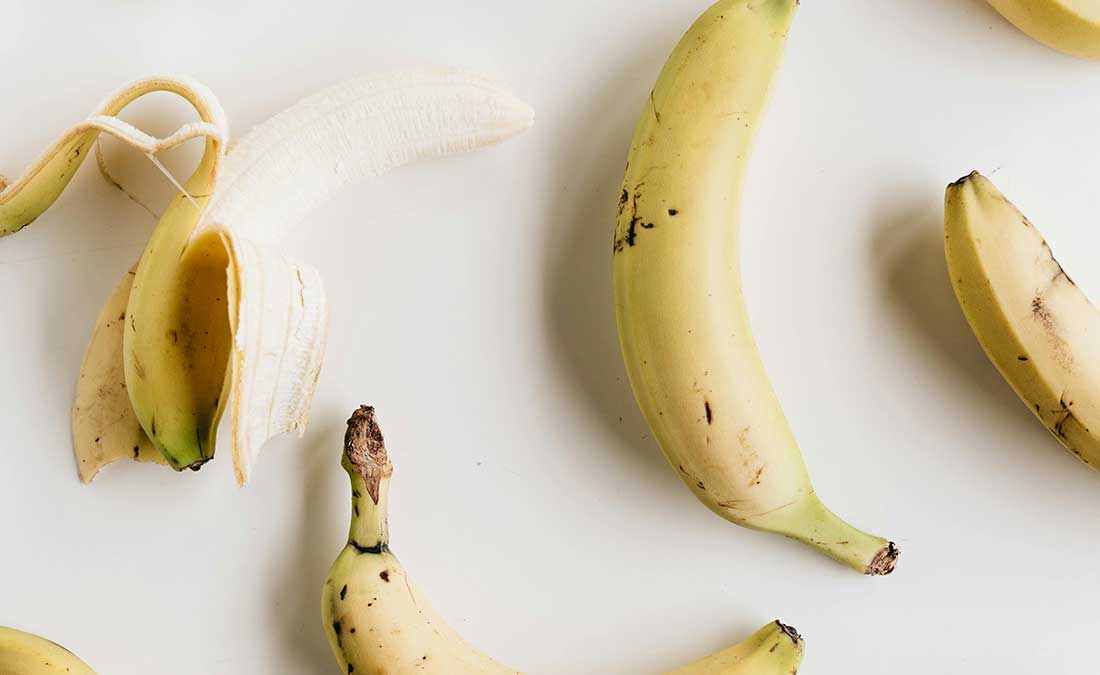

Beyond their potassium fame, bananas are packed with magnesium—both minerals help relax overstressed muscles. Magnesium deficiency is linked to restless leg syndrome, which can seriously interfere with quality sleep. Bananas also contain tryptophan, adding another layer of sleep support.
The Soothing Sips and Treats
7. Herbal Tea

A warm cup of herbal tea creates the perfect wind-down ritual. Chamomile has been successfully used for insomnia for thousands of years, while peppermint reduces stress and promotes sleep. Even decaf green tea offers benefits through theanine, an amino acid that helps reduce stress and promote relaxation.
Choose caffeine-free varieties and make it part of your evening routine about an hour before bed.
8. Tart Cherry Juice

This is one of the few natural food sources of melatonin. In studies, adults who drank tart cherry juice concentrate for just one week had higher melatonin levels and reported sleeping longer and more soundly compared to a placebo group.
Sip 4-6 ounces about an hour before bed for best results.
9. Dark Chocolate

Good news for chocolate lovers: a small square (about 1 ounce) of dark chocolate can actually support sleep. It’s rich in magnesium for muscle relaxation and contains serotonin precursors your body uses to make melatonin. Choose varieties with at least 70% cocoa and enjoy earlier in the evening to avoid any caffeine interference.
Let’s be honest—sometimes a little chocolate is exactly what you need after a long day.
Simple Ways to Work These Into Your Evening
- Make walnut-crusted salmon for dinner
- Blend oats and kiwi into a creamy bedtime smoothie
- Pair fresh kiwi with a handful of walnuts for a satisfying evening snack
- Warm up with a glass of milk sprinkled with cinnamon
- Sip tart cherry juice about an hour before bed
- Enjoy a square of dark chocolate earlier in the evening for a magnesium boost
Start Small, Sleep Better
You don’t need to overhaul your entire diet—just make a few strategic evening swaps. Trade late-night chips for tart cherry juice, replace phone scrolling with a calming cup of chamomile tea, or end dinner with kiwi and dark chocolate instead of heavy dessert. Small, realistic changes compound into dramatically better rest.
Quality sleep isn’t a luxury—it’s your ultimate performance tool. By weaving even a few of these foods into your evening routine, you can fall asleep faster, sleep more deeply, and wake up ready to tackle whatever comes your way, without relying on quick fixes or sleep aids that leave you groggy.
Which sleep-supporting food will you try tonight?
This article has been updated since its previous publication date in August 2022.